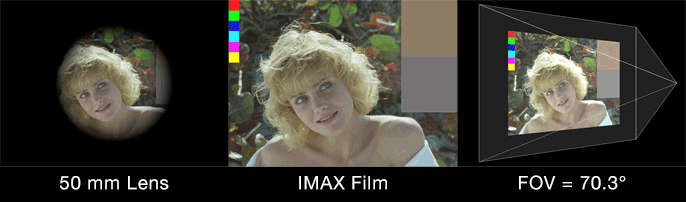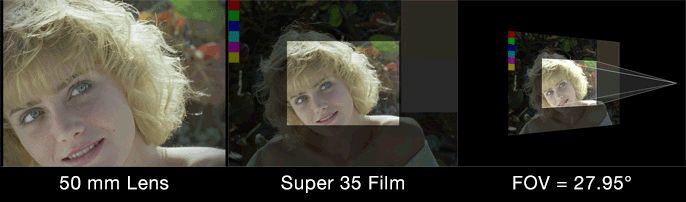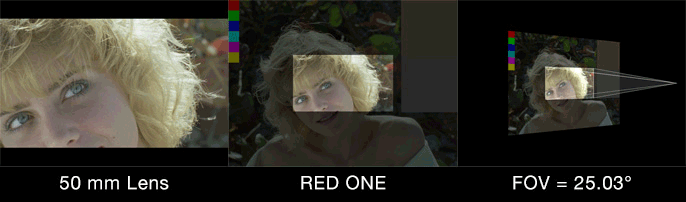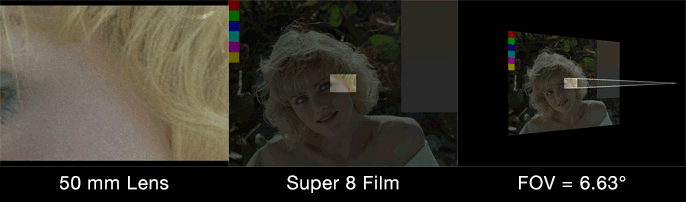WHAT IS FILM BACK AND WHY DO I NEED TO KNOW?
“Film back” is common terminology for the dimensions of a film frame’s or electronic sensor’s imaging area. Focal length is the optical magnification power of a lens. The field of view (FOV) (aka angle of view or viewing frustum angle) will be different on cameras with the same film back sizes using lenses of different focal lengths. The FOV will also be different if the cameras use lenses with the same focal lengths, but have different film back sizes. FOV is determined by the relationship between film back and focal length.
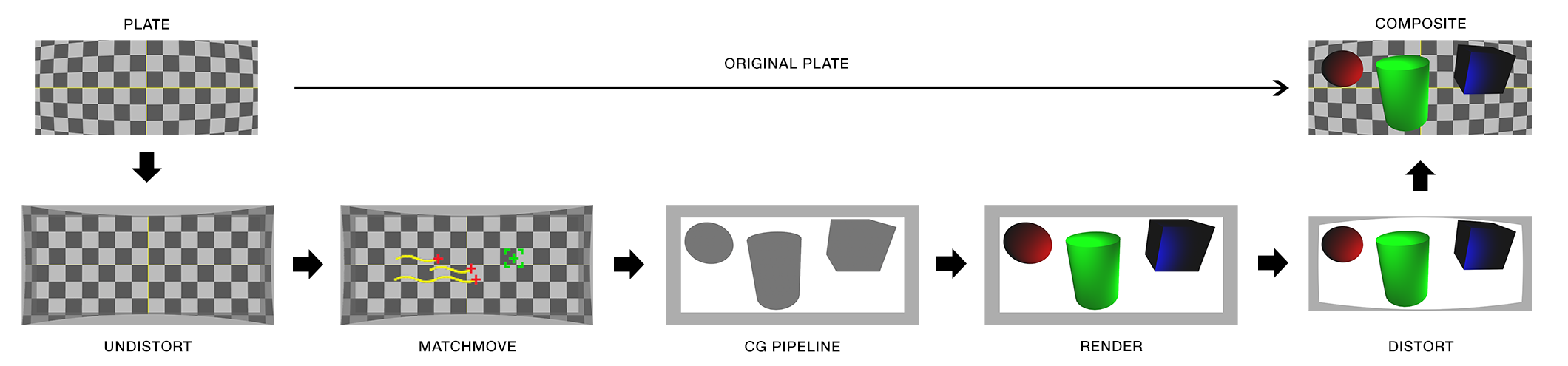
In the discipline of 3D camera tracking the best camera solves are generated when the artist inputs the actual lens focal length and camera film back size used. With these two variables the software can accurately calculate the FOV of a recorded frame. If you only know one variable (or neither) the software will calculate an inaccurate solve. Leaving the artist to do a lot of time consuming guess work.
The focal length is generally easy to obtain. It is printed on the barrel of the lens and is normally written down in logs by a camera assistant. Focal length is usually also collected by a visual effects department member if they are present on set. The film back size is not always as easy to obtain. When images are acquired on film the film back size is determined by the film format being used. There are a limited number of acquisition film formats and they are standardized. Digital cameras do not use standardized sensor sizes. The size of a sensor, and more importantly what portion of it is used to record an image, is rarely published by camera manufacturers. When manufacturers do describe the size of their sensors it is usually in comparison to a film format, not the exact dimensions. Some cameras also change the area of their sensor that is used when recording different resolutions. This change is generally referred to as crop factor. Those digital cameras have different effective film back sizes for different formats and this must be accounted for when solving a camera track.
Lens Image Circle and Sensor Imaging Area
Autodesk Maya Camera Angle of View
Panavision Sensor Size & Field of View
RED, Digital and Film Format Size Chart
ARRI ALEXA XT Sensor Areas
Red MX Crop Factors
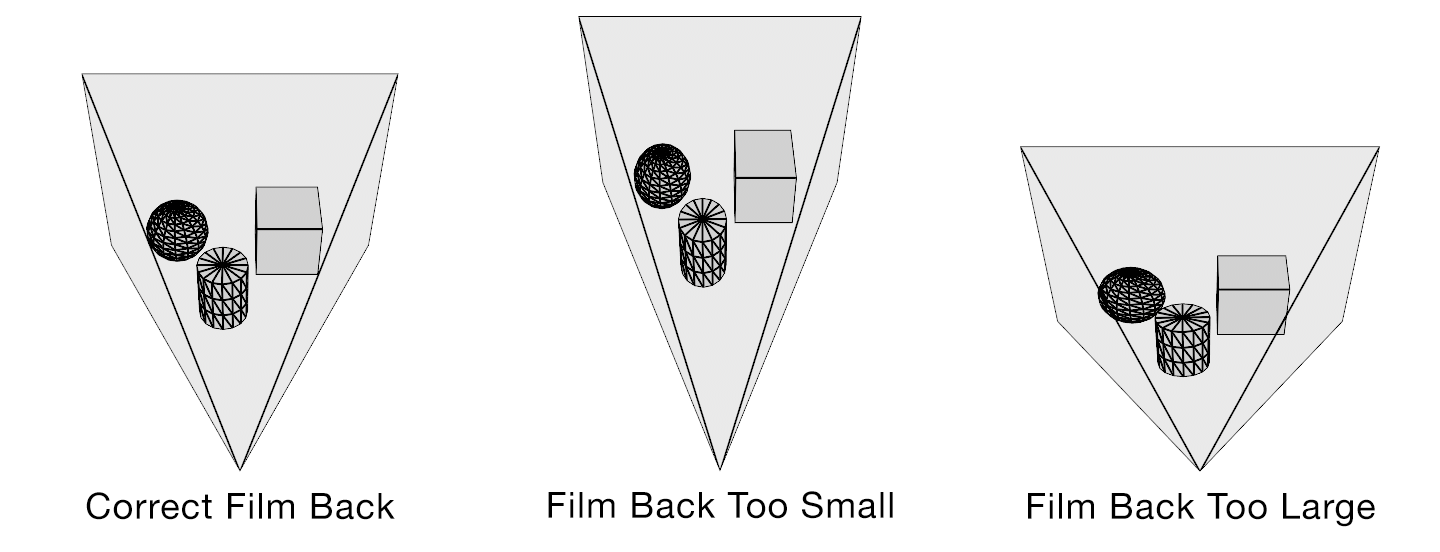
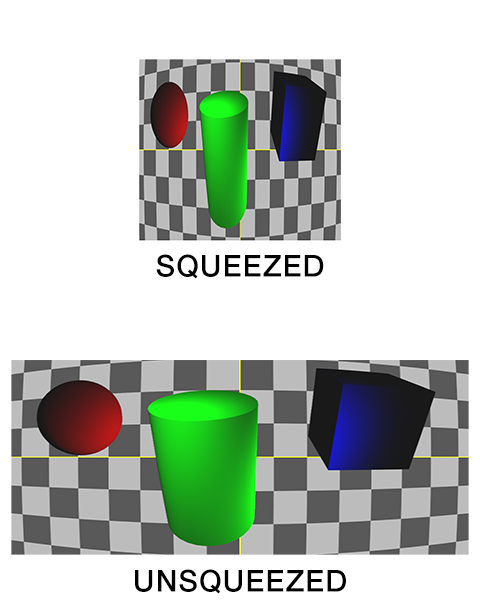
Field of view describes how much of the 3D scene a virtual camera sees. You must know the focal length and film back size so that the correct field of view can be calculated. With the correct field of view a tracked cube in your footage will generate a rectilinear point cloud of a cube in your 3D scene. Exactly matching the cube’s real world proportions. With the wrong field of view the cube will be squashed or stretched. Therefore, not an accurate 3D reconstruction of the photographed object.
HOW DO SOFTWARE PACKAGES EXCHANGE CAMERA DATA?
Most software packages exchange camera information as field of view (FOV). Expressed as a horizontal (most common), vertical or diagonal angle.
WHERE DO I FIND CAMERA SETTINGS / PROPERTIES / ATTRIBUTES IN MY SOFTWARE?
3D Equalizer
SynthEyes
Shot > Edit Shot “Back Plate”
Boujou
Setup > Edit Camera > Advanced “Filmback Width/Height”
PFTrack
https://vimeo.com/channels/pftrack/85934502
3ds Max
Aperture Width
http://www.designimage.co.uk/3dsmax_filmback/
Softimage
Camera Property Editor
Houdini
Camera Object Parameters
Match Houdini camera lenses to the real world
Modo
Camera Item
Cinema 4D
3D Camera Properties
http://www.maxon.net/support/documentation.html
Lightwave
http://forums.newtek.com/showthread.php?87642-Film-Back
Camera Properties
Advanced Camera
Blender
Camera
http://blenderartists.org/forum/archive/index.php/t-104137.html
Nuke
Camera
CameraTracker
Camera Film Back Presets
After Effects
Camera Settings
Virtual Cinematography in After Effects
Fusion
Camera 3D, Aperture (page 9)
Flame
3D Camera Parameters